Here are the latest predictions for June, July, August for temperature and precipitation by the CPC (see below). In the Pacific Northwest, the NWS is predicting warmer than normal temperature (reddish color), but had no reason to predict anything different than normal for precipitation (white or equal changes (EC) of above or below normal precipitation). They were going for a higher probability of warm temperatures in California.
I should note that this forecasts are manual/subjective products, based on forecaster judgement, a variety of statistical tools, the output from extended-range models,the current state of El Nino/La Nina and the cycles like the Pacific Decadal Oscillation, and other sources of information. Sort of the meteorological version of sausage making---you might be surprised what goes into it.
Most Northwesterners would welcome warmer summer and we generally don't get much summer precipitation anyway (and our snowpack is in good shape), so this looks like a favorable forecast for us.
But can you believe such seasonal forecasts, even this close to summer? Do they have any real skill?
The answer: skill is marginal at best.
Editorial: You would think that the National Weather Service would have good verification statistics available on their web site for their long-range predictions, but as with most product verification, their offerings are weak or non-existent. They have an interactive verification tool that does not work ( I have tried on several platforms). Providing the public with good verification information about their forecasts should be a priority for the National Weather Service; they seem to give this task little resource and don't maintain what they have.
So, let's look at what they do have. First, how well did the summer seasonal forecasts go during the last three summers over the Pacific Northwest?
First, 2011. Left panels are for temperature, right panels precipitation. Red indicates above normal temperatures, blue-below normal temperatures) Green above normal precipitation, yellow, below normal precipitation. The upper panels are the official forecasts, the bottom panels are observed conditions.
For the Northwest, they missed the observed, cooler than normal temperatures. Precipitation was better, but again summer precipitation is not a significant parameter around here.
2012? They did not forecast temperature conditions to be different from climatology, but it turned out to be colder than normal. Precipitation was wetter than normal and they were going dry.
2013 was perhaps a bit better. The dry conditions in the the far SE interior of the Northwest were caught, but not the wetter coast and warmer remainder.
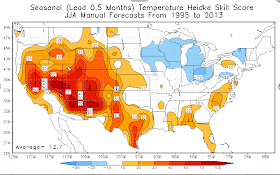
But don't get too depressed about this. Our skill for predicting seasonal weather over the Northwest is considerably better during the winter, particularly during strong El Nino and La Nina years. For example, here is the same figure as above for January, February and March; western Washington is one of the most predictable places in the nation!
And new prediction tools, like the advancing Climate Forecast System (CFS) numerical modeling system, will progressively improve in time. In fact, I am working with others at the UW to build a seasonal prediction capability combining high-resolution modeling with the NWS global CFS system. Early results are promising and we are looking for funding now to push this forward.

.gif)









.gif)































.png)

.jpg)
.jpg)
